As we embark on Learning About Personal Finance 2024, let’s dive into a world of financial knowledge and practical strategies. This guide will empower you to navigate the complexities of personal finance with confidence and clarity.
From budgeting and saving to investing and retirement planning, we’ll cover every aspect of managing your finances effectively. Get ready to transform your financial future, starting today.
Personal Finance Fundamentals

Personal finance is the management of your financial resources, including income, expenses, savings, and investments. It’s essential for financial well-being and achieving your financial goals.
Key concepts include:
- Budgeting:Tracking your income and expenses to ensure you live within your means.
- Saving:Setting aside a portion of your income for future needs or goals.
- Investing:Using your savings to grow your wealth over time through investments like stocks, bonds, or real estate.
Importance of Financial Literacy
Financial literacy is crucial for making informed financial decisions. It empowers you to:
- Understand your financial situation and make sound financial plans.
- Avoid costly financial mistakes and protect yourself from financial risks.
- Achieve your financial goals, such as buying a home, retiring comfortably, or saving for your children’s education.
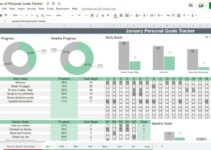
Budgeting and Expense Tracking: Learning About Personal Finance 2024
Budgeting and expense tracking are crucial aspects of personal finance management. They enable you to plan your income and expenses, track your financial progress, and make informed decisions about your spending habits.
There are various budgeting methods available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include:
Zero-Based Budgeting
- Every dollar of income is allocated to a specific category, such as expenses, savings, or investments.
- Helps prevent overspending and encourages responsible financial planning.
- Can be time-consuming and requires discipline.
Envelope Budgeting
- Cash is allocated into different envelopes for each category, such as groceries, entertainment, or gas.
- Helps control spending by limiting access to funds.
- May not be practical for all expenses, such as online purchases.
50/30/20 Rule
- 50% of income is allocated to essential expenses (housing, food, transportation), 30% to discretionary expenses (entertainment, dining out), and 20% to savings and investments.
- Simple and easy to follow.
- May not be suitable for individuals with irregular income or high expenses.
Once you have chosen a budgeting method, the next step is to create a realistic budget and track your expenses. Here are some tips:
- Set financial goals:Determine your short-term and long-term financial objectives.
- Track your income and expenses:Use a budgeting app, spreadsheet, or notebook to record all your income and expenses.
- Categorize your expenses:Group your expenses into categories such as housing, food, transportation, entertainment, and savings.
- Adjust your budget as needed:Review your budget regularly and make adjustments based on your financial situation and goals.
There are numerous tools and resources available to help you with budgeting and expense tracking. These include:
- Budgeting apps:Mint, YNAB, EveryDollar
- Spreadsheets:Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets
- Notebooks:Physical or digital notebooks for manual tracking
By following these tips and utilizing the available tools, you can effectively manage your finances, achieve your financial goals, and secure your financial well-being.
Saving and Investing
Saving and investing are two crucial aspects of personal finance. Saving refers to setting aside a portion of your income for future use, while investing involves using that money to grow your wealth over time.
Setting Financial Goals and Choosing Savings and Investment Vehicles
Before you start saving or investing, it’s essential to set financial goals. This could include saving for a down payment on a house, funding your retirement, or building an emergency fund. Once you have clear goals, you can choose the appropriate savings and investment vehicles.
Savings accounts, money market accounts, and certificates of deposit (CDs) are common savings vehicles that offer varying levels of liquidity and returns. Investment vehicles like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds provide opportunities for growth but also carry varying levels of risk.
Diversifying Investments and Managing Risk
Diversification is a key strategy for managing risk in your investment portfolio. By spreading your investments across different asset classes and investment vehicles, you reduce the impact of any one investment performing poorly. Risk management involves assessing your tolerance for risk and adjusting your investment strategy accordingly.
For example, if you have a low tolerance for risk, you may want to invest more in bonds than in stocks.
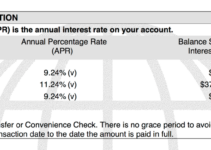
Debt Management and Credit
Debt and credit play significant roles in personal finances. Understanding the different types of debt and their impact, as well as strategies for managing debt and improving credit scores, is crucial for financial well-being.
Types of Debt
- Secured debt:Backed by collateral, such as a mortgage or car loan.
- Unsecured debt:Not backed by collateral, such as credit card debt or personal loans.
- Good debt:Used to invest or improve one’s financial position, such as student loans or business loans.
- Bad debt:Used for consumption or non-essential purchases that do not provide long-term value.
Impact of Debt
- Increased financial burden:Debt payments can reduce disposable income and strain budgets.
- Reduced savings and investment opportunities:Debt payments divert funds that could be used for savings or investments.
- Lower credit score:High levels of debt and missed payments can negatively impact credit scores, making it harder to qualify for loans or favorable interest rates.
Debt Management Strategies
- Create a budget:Track income and expenses to identify areas where spending can be reduced.
- Prioritize debt repayment:Focus on paying off high-interest debts first to save on interest charges.
- Consider debt consolidation:Combine multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate to simplify repayment.
- Negotiate with creditors:Contact creditors to explore options for lower interest rates or extended payment plans.
Improving Credit Scores
- Make payments on time:Payment history is the most significant factor in credit scores.
- Keep credit utilization low:Use less than 30% of available credit limits to demonstrate responsible credit usage.
- Avoid opening multiple new credit accounts:Too many credit inquiries can lower scores.
- Monitor credit reports regularly:Check for errors or fraudulent activity that could impact scores.
Consequences of Poor Credit Management
- Difficulty qualifying for loans:Low credit scores can make it harder to obtain loans or credit cards.
- Higher interest rates:Borrowers with poor credit scores may face higher interest rates on loans.
- Limited access to financial products:Low credit scores can restrict access to financial products, such as mortgages or credit cards.
- Damage to reputation:Poor credit management can damage an individual’s reputation and make it difficult to obtain employment or housing.
Retirement Planning

Retirement planning is crucial for securing your financial well-being during your golden years. It involves setting aside funds and making wise investments to ensure a comfortable retirement lifestyle. Benefits of retirement planning include:
- Financial security during retirement
- Peace of mind knowing you have a nest egg
- Potential for tax savings
- Maintaining your desired lifestyle in retirement
Different Retirement Accounts
Various retirement accounts offer different tax advantages and investment options. Some common types include:
- 401(k) plans:Employer-sponsored plans that allow pre-tax contributions, reducing your current taxable income.
- IRAs (Individual Retirement Accounts):Tax-advantaged accounts that allow you to contribute after-tax or pre-tax funds.
- Roth IRAs:Post-tax contributions grow tax-free, allowing tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
- Annuities:Contracts that provide a guaranteed stream of income for a specified period.
Investment Options
Within retirement accounts, you can choose from various investment options, such as:
- Stocks:Represent ownership in a company and have the potential for high returns but also higher risk.
- Bonds:Loans made to companies or governments, offering lower returns but generally lower risk.
- Mutual funds:Professionally managed baskets of stocks or bonds, providing diversification.
- ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds):Track specific indexes or sectors, offering low costs and diversification.
Creating a Personalized Retirement Plan, Learning About Personal Finance 2024
To create a personalized retirement plan, consider the following steps:
- Estimate your retirement expenses:Determine your desired lifestyle and estimate your expenses in retirement.
- Set a retirement goal:Calculate the amount you need to save to meet your expenses.
- Choose retirement accounts:Select the retirement accounts that best align with your financial situation and tax preferences.
- Determine your investment strategy:Decide on an investment mix that aligns with your risk tolerance and time horizon.
- Monitor and adjust:Regularly review your plan and make adjustments as needed based on market conditions and your financial situation.
Insurance and Risk Management
Insurance plays a crucial role in financial protection, providing a safety net against unforeseen events and mitigating financial risks. It helps individuals and businesses safeguard their assets, income, and overall financial well-being.
There are various types of insurance policies available, each designed to cover specific risks and provide tailored protection. Understanding these policies and assessing individual needs is essential for making informed decisions about insurance coverage.
Types of Insurance Policies
- Health Insurance:Covers medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription drugs.
- Life Insurance:Provides financial support to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder’s death.
- Disability Insurance:Replaces lost income if the policyholder is unable to work due to illness or injury.
- Property Insurance:Protects homes, vehicles, and other personal property against damage or loss.
- Liability Insurance:Covers legal claims for damages or injuries caused to others.
Assessing Insurance Needs
To determine appropriate insurance coverage, individuals should consider factors such as their age, health, lifestyle, financial situation, and specific risks associated with their profession or hobbies. A comprehensive review of assets, liabilities, and potential financial vulnerabilities is essential.
Choosing Appropriate Policies
When selecting insurance policies, it’s important to compare coverage options, deductibles, premiums, and exclusions. Understanding the terms and conditions of each policy is crucial to ensure it aligns with individual needs and provides adequate protection.
Consulting with an insurance professional can provide valuable guidance and help individuals make informed decisions about their insurance coverage. They can assess risks, recommend suitable policies, and assist in navigating the insurance landscape.
Tax Planning and Optimization
Taxation plays a significant role in personal finances, affecting income, investments, and retirement savings. Understanding the basics of taxation and implementing strategies for tax planning can help individuals minimize their tax liability and optimize their financial well-being.
Tax Basics and Impact
Taxes are mandatory payments made to government entities, such as federal, state, and local governments. They are levied on various sources of income, including wages, salaries, investments, and property. Taxes can be progressive, meaning they increase as income rises, or flat, meaning they are the same for all taxpayers regardless of income.
Understanding the different types of taxes and how they apply to your financial situation is crucial for effective tax planning.
Tax Planning Strategies
Tax planning involves taking proactive measures to reduce tax liability while complying with all applicable laws. Some common strategies include:
- Maximizing Tax-Advantaged Accounts:Contributing to tax-advantaged accounts, such as 401(k)s, IRAs, and 529 plans, allows for tax-free growth of investments and potential tax savings upon withdrawal.
- Itemizing Deductions:Itemizing deductions on tax returns can reduce taxable income, resulting in lower tax liability. Deductions can include mortgage interest, property taxes, charitable donations, and medical expenses.
- Claiming Tax Credits:Tax credits directly reduce tax liability, dollar for dollar. Common tax credits include the child tax credit, earned income tax credit, and education tax credits.
- Tax Loss Harvesting:Selling investments that have decreased in value can generate capital losses, which can be used to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income.
Resources for Tax Preparation and Filing
Tax preparation and filing can be complex, but there are resources available to assist individuals.
- Tax Software:Commercial tax software can guide users through the tax preparation process, perform calculations, and help identify deductions and credits.
- Tax Preparers:Certified public accountants (CPAs) and enrolled agents (EAs) are licensed professionals who can prepare and file tax returns for individuals and businesses.
- IRS Resources:The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides a wealth of information, including publications, forms, and online tools to help taxpayers understand and comply with tax laws.
By implementing tax planning strategies and utilizing available resources, individuals can optimize their financial well-being and minimize their tax liability.
Financial Planning for Life Events
Life events can significantly impact your financial situation, so it’s crucial to consider them in your financial planning. Major events such as marriage, childbirth, and career changes can alter your income, expenses, and financial goals.
Adjusting Financial Plans for Life Events
To accommodate life events, you may need to adjust your financial plan. This could involve:
- Revising your budget to account for increased expenses or reduced income.
- Reviewing your investment strategy to ensure it aligns with your new financial goals.
- Adjusting your insurance coverage to protect against potential risks associated with the event.
Importance of Regular Review and Updates
Your financial plan should be a living document that you review and update regularly. Life events can occur unexpectedly, and it’s essential to ensure your plan is up-to-date and reflects your current circumstances. By doing so, you can make informed financial decisions and minimize the impact of life events on your financial well-being.
Financial Technology and Tools
Financial technology, commonly known as fintech, is revolutionizing the way we manage our personal finances. It offers a wide range of tools and services that can help us budget, invest, and plan for the future more effectively.
Fintech tools come in various forms, including budgeting apps, investment platforms, and credit monitoring services. Budgeting apps like Mint and YNAB allow you to track your income and expenses, set financial goals, and create budgets. Investment platforms like Robinhood and Acorns make it easy to invest in stocks, bonds, and other financial assets.
Credit monitoring services like Credit Karma and Experian provide access to your credit reports and scores, helping you stay on top of your credit health.
Benefits of Using Financial Technology
- Convenience: Fintech tools are accessible anytime, anywhere, making it easy to manage your finances on the go.
- Automation: Many fintech tools offer automation features, such as automatic bill payments and savings transfers, which can save you time and effort.
- Personalization: Fintech tools can be tailored to your specific financial needs and goals, providing personalized insights and recommendations.
Limitations of Using Financial Technology
- Data Security: Fintech tools require access to your financial data, which raises concerns about data security. It’s important to choose reputable companies with strong security measures.
- Cost: Some fintech tools may charge subscription fees or transaction fees, which can add up over time.
- Overreliance: Relying too heavily on fintech tools can lead to a lack of financial literacy and an over-dependence on technology.
Despite these limitations, financial technology has the potential to greatly enhance our ability to manage our personal finances. By understanding the role of fintech and using it wisely, we can take control of our finances and achieve our financial goals.
Resources and Support for Personal Finance

Personal finance can be a complex and overwhelming topic, but there are numerous resources available to help you learn and manage your finances effectively. From books and websites to financial advisors, there are many options to choose from.
Books and Websites
There are countless books and websites dedicated to personal finance, covering a wide range of topics. Some popular books include “The Total Money Makeover” by Dave Ramsey, “The Psychology of Money” by Morgan Housel, and “Rich Dad Poor Dad” by Robert Kiyosaki.
Reputable websites like NerdWallet, The Balance, and Investopedia offer comprehensive articles, calculators, and tools to help you make informed financial decisions.
Financial Advisors
If you’re struggling to manage your finances on your own or have complex financial needs, consider seeking professional guidance from a financial advisor. A qualified advisor can provide personalized advice tailored to your specific situation, help you create a financial plan, and guide you through major financial decisions.
Staying Informed
It’s essential to stay informed about financial news and trends to make informed decisions about your finances. Follow reputable financial publications, listen to podcasts, and attend webinars to keep up with the latest developments in the financial world. Understanding the economic climate and financial markets can help you make better choices and adapt to changing circumstances.
Closing Notes
Learning About Personal Finance 2024 has been an enlightening journey. By embracing the principles Artikeld in this guide, you’ll gain the skills and knowledge to make informed financial decisions, achieve your financial goals, and secure your financial well-being.
Question Bank
What is the most important aspect of personal finance?
Financial literacy is crucial as it empowers you to understand and manage your finances effectively.
How can I create a realistic budget?
Track your expenses, identify areas where you can cut back, and allocate funds wisely.
What is the difference between saving and investing?
Saving refers to setting aside money for short-term goals, while investing involves using money to grow your wealth over time.